|
JSR-275 - Measurements and Units Specification | ||||||||
| PREV PACKAGE NEXT PACKAGE | FRAMES NO FRAMES | ||||||||
See:
Description
| Interface Summary | |
|---|---|
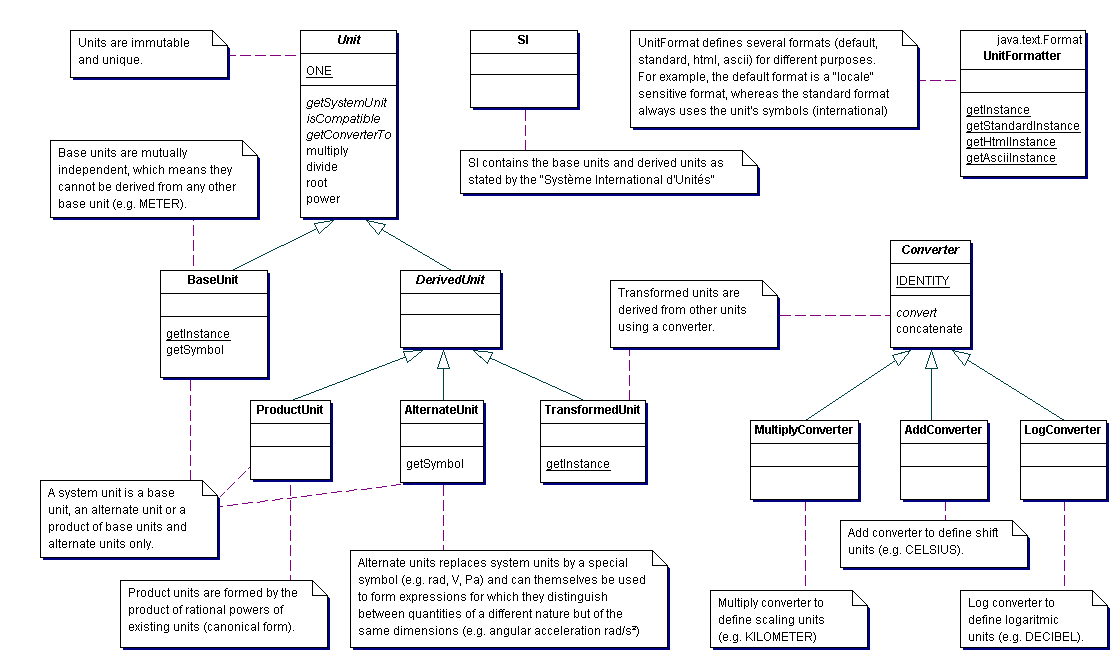
| Dimension.Model | This interface represents the mapping between base units
and dimensions. |
| Class Summary | |
|---|---|
| AlternateUnit<Q extends Quantity> | This class represents the units used in expressions to distinguish between quantities of a different nature but of the same dimensions. |
| BaseUnit<Q extends Quantity> | This class represents the building blocks on top of which all others units are created. |
| CompoundUnit<Q extends Quantity> | This class represents the multi-radix units (such as "hour:min:sec"). |
| DerivedUnit<Q extends Quantity> | This class identifies the units created by combining or transforming other units. |
| Dimension | This class represents the dimension of an unit. |
| NonSI | This class contains units that are not part of the International System of Units, that is, they are outside the SI, but are important and widely used. |
| ProductUnit<Q extends Quantity> | This class represents units formed by the product of rational powers of existing units. |
| SI | This class contains SI (Système International d'Unités) base units, and derived units. |
| TransformedUnit<Q extends Quantity> | This class represents the units derived from other units using
converters. |
| Unit<Q extends Quantity> | This class represents a determinate quantity (as of length, time, heat, or value) adopted as a standard
of measurement. |
| UnitFormat | This class provides the interface for formatting and parsing units. |
Provides support for programatic unit handling.
SI class (Système International d'Unités) and
about 50 non-standard units are available through the
NonSI class.
import javax.measure.Measurable;
import javax.measure.Measure;
import javax.measure.unit.*;
import javax.measure.quantity.*;
import static javax.measure.unit.SI.*;
import static javax.measure.unit.NonSI.*;
import static javax.measure.unit.Dimension.*;
public class Main {
public void main(String[] args) {
// Conversion between units.
System.out.println(KILO(METER).getConverterTo(MILE).convert(10));
// Retrieval of the system unit (identifies the measurement type).
System.out.println(REVOLUTION.divide(MINUTE).getSystemUnit());
// Dimension checking (allows/disallows conversions)
System.out.println(ELECTRON_VOLT.isCompatible(WATT.times(HOUR)));
// Retrieval of the unit dimension (depends upon the current model).
System.out.println(ELECTRON_VOLT.getDimension());
}
}
> 6.2137119223733395
> rad/s
> true
> [L]²·[M]/[T]²
Quantity>) to
enforce compile-time checks of units/measures consistency, for example:
Unit<Duration> MINUTE = SECONDS.times(60); // Ok.
Unit<Duration> MINUTE = METER.times(60); // Compile error.
Unit<Pressure> HECTOPASCAL = HECTO(PASCAL); // Ok.
Unit<Pressure> HECTOPASCAL = HECTO(NEWTON); // Compile error.
Measurable<Duration> duration = Measure.valueOf(2, MINUTE); // Ok.
Measurable<Duration> duration = Measure.valueOf(2, CELSIUS); // Compile error.
long milliseconds = duration.longValue(MILLI(SECOND)); // Ok.
long milliseconds = duration.longValue(POUND); // Compile error.
|
JSR-275 - Measurements and Units Specification | ||||||||
| PREV PACKAGE NEXT PACKAGE | FRAMES NO FRAMES | ||||||||